Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking Studies of C-3 Substituted Coumarin Analogs to Explore their Anti-Proliferative Potential
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.1.6Keywords:
ADMET, Coumarin, Cytotoxicity, Molecular DockingAbstract
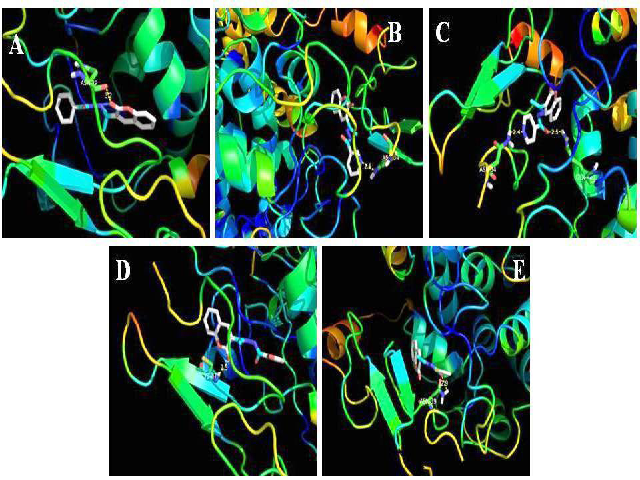
A series of C-3 substituted coumarin analogs were synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro cytotoxicity. These analogs showed good AD-MET properties and passed Lipinski’s filters for drug-likeness. Some of these synthesized com-pounds, showed potent anti proliferative activity against human cancer cell lines MCF-7, HeLa and SCC-40. 3ACFA and 3ACTA were found active against HeLa and SCC-40 cell lines re-spectively with GI50 value for 3ACFA against HeLa as 36.34 μg/ml while SCC-40 exhibited a GI50 value of 38.92 μg/ml. 3ACTA analog ex-hibited the GI50 value of 25.68 μg/ml against SCC-40. The molecular docking was performed with the active site of cyclooxygenase enzyme and the results were well complemented by the experimental data. The possible binding modes of compounds provided a reasonable explana-tion for the selectivity. These results highlighted that compounds 3ACFA and 3ACTA might be a promising scaffold for cancer therapy.