Unveiling the Effects of Cisplatin and Diallyl Disulfide on MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.3.29Keywords:
Cancer, wound healing, colony formation, apoptosis, cell cycle, HaemolysisAbstract
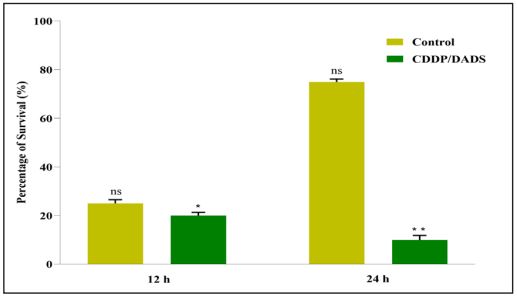
Cancer is one of the most aggressive diseases and is the primary cause of mortality around the world. This can be prevented by combining anti-cancer drugs to reduce the resistance to monotherapy and thereby reduce the toxic effects. Cytotoxic anticancer drugs can potentially elicit cancer cell death by apoptosis or necrosis. Our present study aimed to investigate the combined cytotoxic potential of cisplatin (CDDP) and diallyl disulfide (DADS) on MDAMB-231 breast cancer cell lines. The clonogenic assay was also performed to assess the effects of the drug on the proliferation of breast cancer cells. The results showed that CDDP/DADS (CDDP and DADS) markedly inhibited cell proliferation and significantly reduced the colony formation potential, migration, and invasion abilities of MDA-MB-231 cells. The apoptosis assay confirmed that cell death was through an apoptotic pathway. Cell cycle analysis results indicated that the combination effect of the drugs resulted in arresting cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. Further, the haemolytic assay revealed that the CDDP/DADS is nontoxic to RBCs. In conclusion, combining these two drugs inhibits the oncogenic properties of TNBC cells, including their growth, survival, migration, and invasiveness.