Molecular Docking Analysis of Christanoate and Christene from Christia vespertilionis Plants as Potential Inhibitors of Covid-19
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.2.22Keywords:
SARS-CoV-2, Christia vespertilionis, molecular docking, Covid-19Abstract
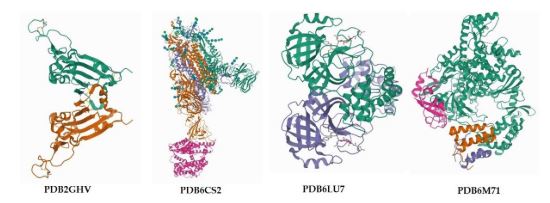
Covid-19 is a global pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus that caused mortality and world economic collapse. It is almost impossible to break the chain of infection with no intervention except vaccines to prevent worsening symptoms and to build herd immunity in people. Efforts to discover a therapeutic drug to combat the virus are still ongoing. Various medicinal phyto constituents are also researched for their pharmacological action as antiviral agents against Covid-19. This study explored the antiviral potential of Christia vespertilionis bio active compounds (christene and christanoate) for treating Covid-19 using molecular docking analysis. The Covid-19 protein crystal structures (PDB ID: 6LU7, PDB ID: 6CS2, PDB ID: M1D, PDB ID: 2GHV and PDB ID: 6M71) obtained from the protein data bank were docked to christene and christanoate. The analyses were carried out using the Autodock tool 1.5.6. The control docking was done using favipiravir as the reference drug. The binding interaction of the protein and ligand was observed using the Biovia Discovery visualizer. The binding affinity and interactions indicate that the observed compounds have antiviral action suggesting their potential as Covid-19 inhibitors and can be further considered for therapeutic applications.