Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Leaf Methanolic Extracts of Adhatoda vasica (L.) Nees and Psidium guajava L. by GC-MS Profiling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.3.32Keywords:
Adhatoda vasica, Psidium guajava, GC-MS analysis, PhytochemicalsAbstract
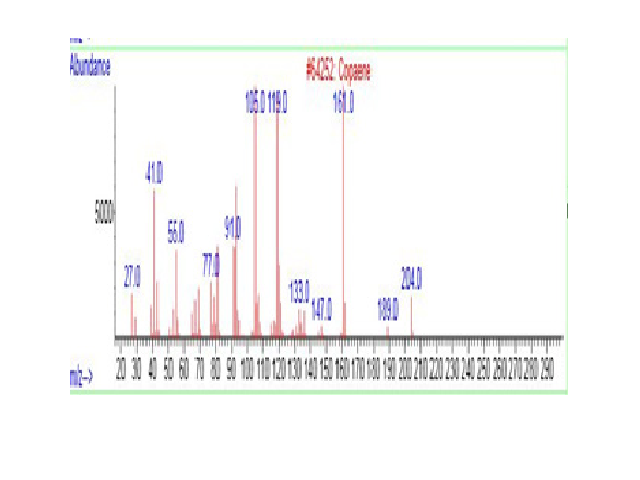
While Adhatoda vasica (Vasaka) is an important medicinal plant used as a remedy for treating bronchitis, tuberculosis and other lung disorders, Psidium guajava (Guava) is used against diabetes, diarrhea, dysentery, gastroenteritis and hypertension. We report here the methanolic extract and phytochemical analysis of both the plants from the leaves using gas-chromatography (GC) and mass spectrometry (MS). Analysis of vasaka revealed the presence of amrinone, a selective phosphodiesterase III inhibitor effective in the treatment of congestive heart failure; silicic acid associated with bone mineralization, collagen synthesis, skin, hair and nails health atherosclerosis, Alzheimer disease, immune booster; arsenous acid used for treating leukemia; methyltris (trimethylsiloxy)silane which is a potent antibacterial compound; tetrasiloxanedecamethyl- that exhibits antifungal activity. Analysis of guava revealed the presence of copaene (a tricyclic sesquiterpene) that has antioxidant activity, caryophyllene oxide which has relaxation effect, humulene that promotes appetite-suppressing effect and used for weight loss, γ-muurolene that is known for its antibacterial activity and also alloaromadendrene, a sesquiterpenoid with anticancer and antibacterial properties. Importantly, it also contains (±)-norephedrine, an appetite suppressant and used for nasal decongestion. Phenylephrine is used to relieve nasal discomfort caused by colds, allergies, and hay fever, and (-)-isolongifolol, an antioxidant. The data show that both the plants have important bioactive molecules that can be further exploited for treating human ailments.