Evaluation of In-vitro Cytoprotective, Wound Healing and Antioxidant Effects of Ocimum sanctum Leaf ExtractChetna
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2021.3.27Keywords:
Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals, Malondialdehyde, Oxidative stress, Cytoprotective, Wound healingAbstract
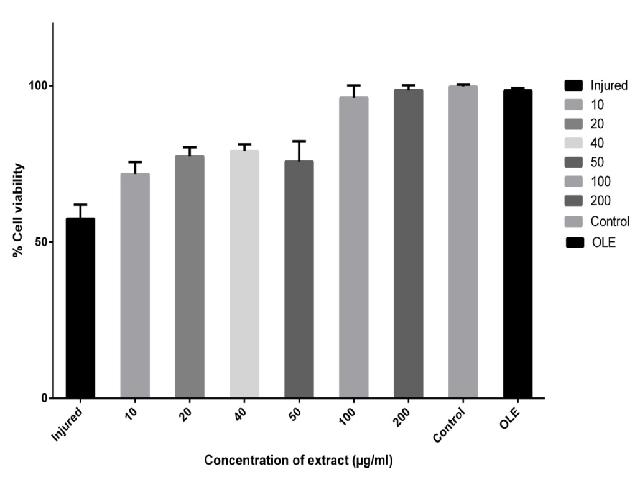
Exposure of renal epithelial cells to Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals leads to cellular injury and play a significant role in the formation of kidney stones. Additionally, lipid peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids further accelerates the generation and progression of the disease. Availability of safe and effective treatment of the disease is the need of hour. The objective of this research work was to evaluate the impact of hydro-alcoholic extract of Ocimum sanctum leaves on renal epithelial cell injury, oxidative stress and wound healing. Renal epithelial cells (Vero cells) were exposed to Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals to cause injury and then injured cells were treated with Ocimum sanctum extract. Cell viability of the treated group was compared against control using MTT assay. Antioxidant potential was evaluated using malondialdehyde content as biomarker. Wound healing potential was evaluated using scratch assay. A significant increase in cell viability and wound closure rate was observed in the treated group compared to that in control group was observed. We observed reduced malondialdehyde content in the treated group as compared with control. It can be concluded that hydro-alcoholic extract of leaves of Ocimum sanctum possesses strong cytoprotective, antioxidant and wound healing potential and can be effective in the prevention and treatment of kidney stones.