Papain Mitigates Carbontetrachloride Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats Via Attenuation of Oxidative StressHemalatha.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2021.3.26Keywords:
Hepatotoxicity, Oxidative damage, Protective role, PapainAbstract
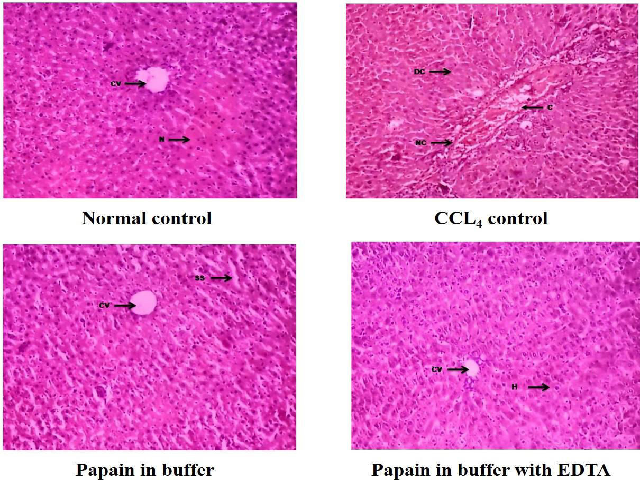
Liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing toxic substances present in the body. Excessive exposure of liver to toxic agents results in hepatic damage. Certain medicinal agents in therapeutic value cause hepatotoxicity in rats due to which withdrawn from the market. In the present study, we evaluated the protective effects of papain (PN) against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Briefly, the rats were divided into four groups of seven animals in each group. Group 1 served as normal control and received water as vehicle. Group 2 received CCl4 0.5 ml/kg intraperitoneally. Group 3 received PN 80mg/kg (p.o, daily) in phosphate buffer for 7 days and CCl4 0.5ml/kg i.p on 7th day. Group IV received PN 80mg/kg (p.o, daily) in phosphate buffer with disodium edentate (EDTA) for 7 days and CCl4 0.5ml/kg i.p on 7th day. The protective effect of PN was measured biochemically and histologically in blood/liver and liver respectively. Treatment with PN significantly (p<0.001) reversed CCl4 induced oxidative hepatic damage which was measured by estimation of superoxide dismutase (SOD), lipid peroxidation (MDA), reduced glutathione (GSH). CCl4 induced elevation in serum hepatic markers (like AST, ALP, ALT, total bilirubin) were significantly reverted in rats by pretreatment with PN. The biochemical observations were paralleled by histopathological findings in rat liver both in CCl4 and treatment groups. In conclusion, Papain attenuates CCl4 induced hepatic damage by mitigating oxidative stress which was confirmed by histology suggesting its use as a protective agent against hepatotoxicants.