Identification of New Alkaloids from Algerian Purslane by HPLC-QTOF-MS and Beneficial Effect of Purslane Enriched with Zinc on Experimental Alzheimer Disease in Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.1.8Keywords:
Alzheimer, Purslane, Zinc, HPLC-QTOF-MS, Amyloid B, AChE, Oxidative stressAbstract
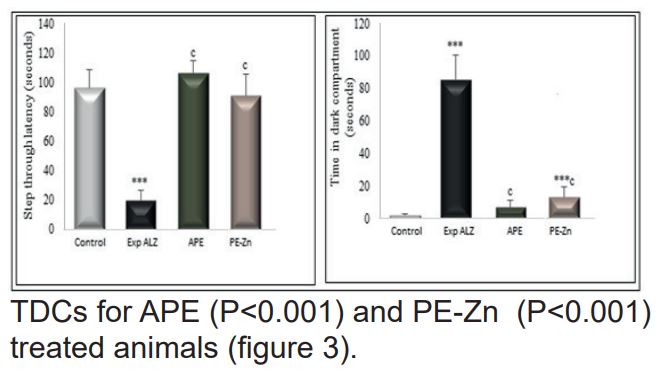
Our study aimed to investigate the im-pact of purslane (P. oleracea) and zinc as a ther-apeutic approach to physiological and biochem-ical alterations induced by Alzheimer disease (ALZ) in rats. For this purpose, 18 males albino Wistar rats were randomly divided into 4 groups (n=6); healthy rats (Control), untreated Alzhei-mer rats (Exp ALZ), Alzheimer rats treated with aqueous purslane extract (APE) and Alzheimer rats treated with purslane extract and zinc (PE-Zn).Various neurological and biological param-eters were estimated and brain Histopathology was observed. Results of study showed an al-teration in passive avoidance learning (PAL) and a significant increase in AChE activity (P<0.01) and protein, WBC, Monocyte, LYM, platelet and MDA levels and decreasing the GSH levels, GST and SOD activities in Exp ALZ group com-pared to control. In the other hand, histopatho-logical analysis recorded a deep modification in brain tissues of Alzheimer rats group compared to control. However, the treatment of ALZ rats by APE and zinc ensured a partial amelioration and correction of the previous parameters. We conclude that the use of purslane seems to be the powerful limited of Alzheimer disease devel-opment or its complications.