Parkinson’s disease Detection Using Tree Based Machine Learning Algorithms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.2.19Keywords:
Parkinson’s Disease (PD), LightGBM, Pearson Correlation, Accuracy, Er-ror Rate, Jupyter NotebookAbstract
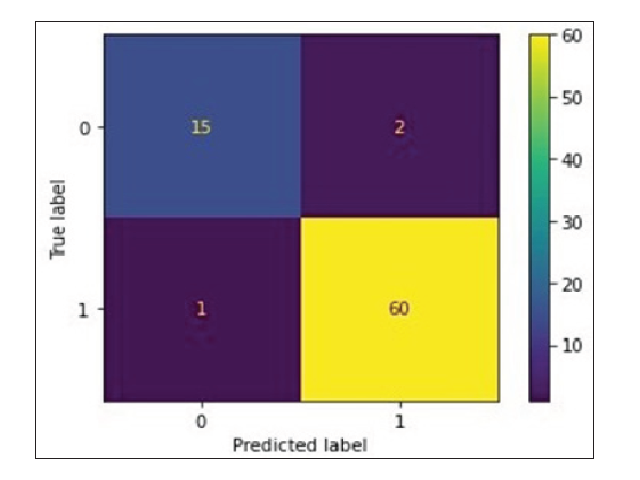
Parkinson’s Disease (PD), also known as primary Parkinsonism is a persistent, idio-pathic, degenerative nervous disorder which re-sults from lack of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta, which is the source of nigrostriatal dopamine pathway with-in the midbrain. The clinical detection relies on motor symptoms recognition. Significant neu-rological damage is already done by the time motor symptom occur. Early detection is nec-essary to stalk the progression of the disease. The problem of detection of PD comes under classification. Several tree-based classification algorithms were applied to the dataset retrieved from UCI machine learning database. The data-set was first split into train and test data. Various models were created using four different algo-rithms. Correlation coefficients were calculat-ed for each of the features in the dataset. The model was fitted with train data obtained after removing highly correlated features. Predictions were made and various parameters were con-sidered for comparison. Accuracy, precision, recall, F1-Score, Youden Index, error rate and specificity were the parameters calculated. Out of the four algorithms (Decision Tree, Random Forest, XGBoost and LightGBM), LightGBM achieved the highest accuracy of 97.43%.