Bio-Decolorization and Degradation of Reactive Blue 222 by a Novel Isolate Kucoria marina CU2005
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.1.5Keywords:
Reactive blue 222, Biodegradation, Kucuria marina, Optimisation, Dye metabolitesAbstract
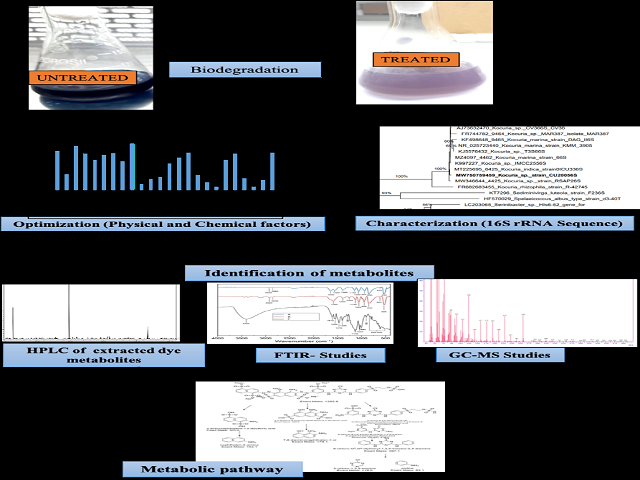
In this study, a novel bacterial strain, Kucoria marina CU2005, was isolated and identified using 16S rRNA gene sequencing from an industrial wastewater sludge sample capable of degrading Reactive Blue 222 (RB222) dye. Batch mode bio stimulation studies were performed with minimal salt media to optimize key physiological parameters for effective decolorization of RB222. When cultured at 35 °C and pH 7 under static conditions, this bacterium decolorized 82 percent of the dye after 24 hours. Decolorization was monitored using UV-vis spectrophotometry. Isolate’s ability to decolorize the complex dye was attributed to its degradation potential rather than a passive surface adsorption. FTIR, HPLC, GC-MS studies were used to confirm microbial dye metabolism. The results indicated breakdown of dye upon decolorization as some peaks were shifted and generation of aromatic amine for monosubstituted benzene ring as intermediates of dye degradation in decolorized solutions. This study has shown the potential of Kucoria marina CU2005 to decolorize RB222 dye at a better pace and efficiency than previously reported bacterial strains. Thus, we propose that our isolated strain can be utilized as a potential dye decolorizer in environmental biotechnology as effluent treatment for decolorization of RB 222.