Simple and Rapid DNA Isolation from Shrimps by Using Single tube extraction buffer with Single step
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.2.21Keywords:
Aquaculture, Shrimp, PCR, SYBR Green assayAbstract
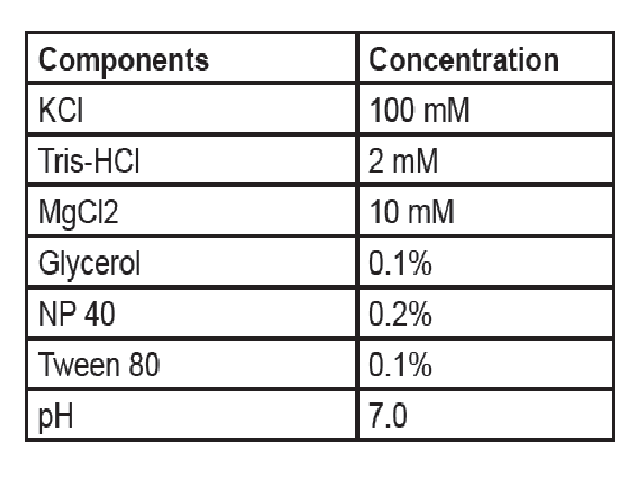
<p style="text-align: justify;">Aquaculture and aquatic animals are important for national food security since they are a good source of animal meat and protein for mankind. Aquaculture is currently the most economically and financially viable option for farmers, so the majority of them are interested in it. In aquaculture, shrimp farming plays a major role and exists in either a freshwater or marine environment for human consumption. Although shrimps are very susceptible to diseases during breeding and farming, these diseases are iden-tified by several methods, i.e., microbiology test, antigen-antibody testand molecular methods. For molecular screening and testing of shrimps, it is necessary to extract nucleic acid, i.e., DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). So many traditional and commercial methods are available on the market for nucleic acid extraction. In our study, we developed a simple, rapid, efficient, and ef-fective nucleic acid extraction method. DNA was isolated from shrimps and shrimp seeds using this method (A260/280 range: 70 ng/uL to 350 ng/uL) and tested using molecular (PCR-Poly-merase Chain Reaction) methods, specifically the SYBR Green assay on Real Time PCR.</p>