Cardiovascular Toxicity of Oral Antidiabetic Drugs and the Efficacy of Natural Organosulfure Compounds from Aged Garlic Extract (AGE)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.4.89Keywords:
Diabetes, Antidiabetic drugs, Toxicity, Diabetic cardiomyopathy, Phototherapeutics, Aged garlic, Organosulfur compoundsAbstract
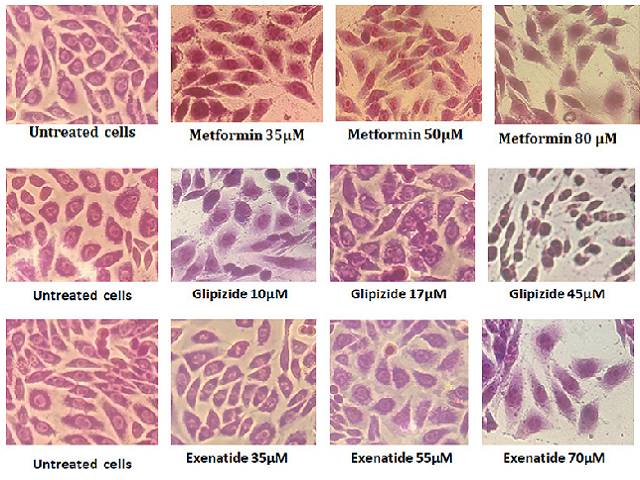
The cardiovascular toxicity of oral antidiabetic drugs has become a major concern for patient with type-II diabetes, which demands investigation of the potential natural products to reduce the toxicity of these drugs and improve their efficacy. In the present study, we investigated the metabolic and oxidative stress of oral antidiabetic drugs on cardiovascular system; we evaluated the antioxidative and cardioprotective efficacy of aged garlic (AGE) against drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Metabolic stress of selected classes of antidiabetic drug classes including; biguanides (BG), sulfonylureas (SU), glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4-I), thiazolidinediones and sodium/glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2) was evaluated by MTT cell viability assay on the H9c2 cardiac cell line. Pre-cytotoxic dose, transition dose and cytotoxic dose of each drug were optimized by MTT assay. The results were further validated by morphological analysis at cardiotoxic doses by giemsa staining and trypan blue dye exclusion assay in a six-well plate experiment. Nuclear alterations and oxidative stress excreted by each drug was evaluated by DAPI and DCFH-DA assay respectively. To evaluate the cardioprotective efficacy of AGE, cell viability assay was performed for each drug co-incubated with 30μM AGE for 48h in MTT plates. The study confirms that SU, DPP-IV and TZD exert metabolic toxicity on cardiac cells by elevating the oxidative stress, morphological, nuclear damage. SGL-2 and GLP-1 were found to be moderately cardiotoxic, while biguanide was found to be cardioprotective. Aged garlic, an antioxidative molecule with stable sulfur compounds was found to exert cardioprotective effect for SU and TZD, it was found to suppress cell death and increase the cell viability by significantly reducing the oxidative stress of antidiabetic drugs. We concluded that aged garlic can be supplemented with anti-diabetic drugs to suppress the cardiotoxic effect of antidiabetic drugs in future drug therapeutics.