Syzygium cumini Protects Diabetic Wistar Rats Against Rosiglitazone-Induced Cardiotoxicity and Hepatotoxicity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.3s.72Keywords:
Alloxan, Antioxidant, Cardiotoxicity, Diabetes, Hepatotoxicity, Jambul, RosiglitazoneAbstract
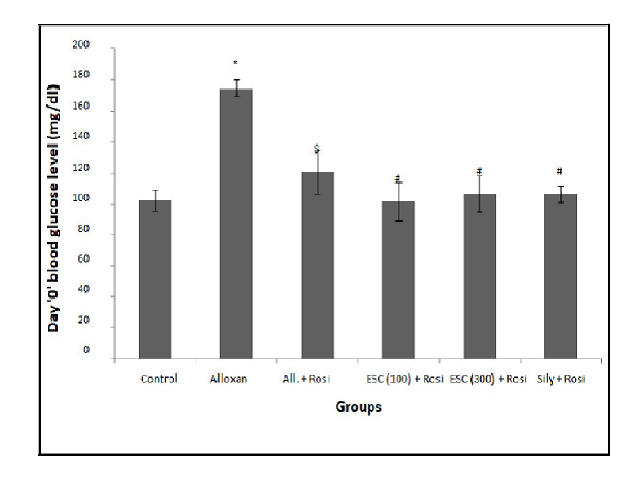
Syzygium cumini (Family: Myrtaceae), is known to show antioxidant, antidiabetic, cardioprotective and hepatoprotective activities in ayurvedic system of medicine. This study aims at determining in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of ethanolic extract of S. cumini (ESC). Effect of ESC on rosiglitazone induced cardiotoxicity and hepatoxicity in alloxaninduced diabetic rats was studied. Results of study indicated that ESC exhibited significant protection against cardiac and hepatic damage caused by rosiglitazone in alloxaninduced diabetes in rats comparable to silymarin, used as reference standard. Cardioprotective and hepatoprotective activity may be attributed to presence of antioxidant activity.