Formulation and Evaluation of Cilnidipine Solid Dispersions and Oral Controlled Release Formulations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.3s.69Keywords:
Cilnidipine, Solid dispersions, Plasdone K-29/32, Controlled release, PEO WSR 303Abstract
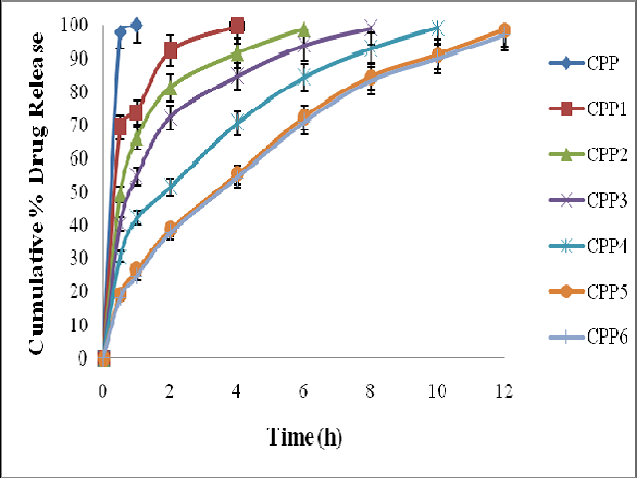
The objective of the present study is to improve the solubility of Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) Class-II drug, Cilnidipine by formulating them as solid dispersions and to make controlled released formulations. Solid dispersions of Cilnidipine were prepared by solvent evaporation technique using plasdone K-29/32. Various physical parameters were evaluated for the prepared solid dispersions. The in vitro drug release studies were performed for the solid dispersions using phosphate buffer pH 6.8. The solid dispersions which showed maximum drug release were selected for the preparation of oral controlled release formulations. Tablets were prepared using Cilnidipine solid dispersions and varying concentrations of polyethylene oxide (PEO) WSR 303 by direct compression technique. Pre and post-compression parameters were evaluated along with in vitro drug release studies. In vitro dissolution studies revealed that solid dispersion CP3 containing Cilnidipine and plasdone K-29/32 in 1:3 ratios showed faster drug release. Formulation CPP5 containing CP3 solid dispersion with 25% w/w of PEO WSR 303 showed prolonged drug release up to 12h. The solubility of Cilnidipine was enhanced using plasdone K-29/32 and the drug release was delayed using PEO WSR 303 as polymer.