Design and development of itraconazole loaded nanosponges for topical drug delivery
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.3s.76Keywords:
Itraconazole, β-cyclodextrin, Nanosponges, Diffusion rateAbstract
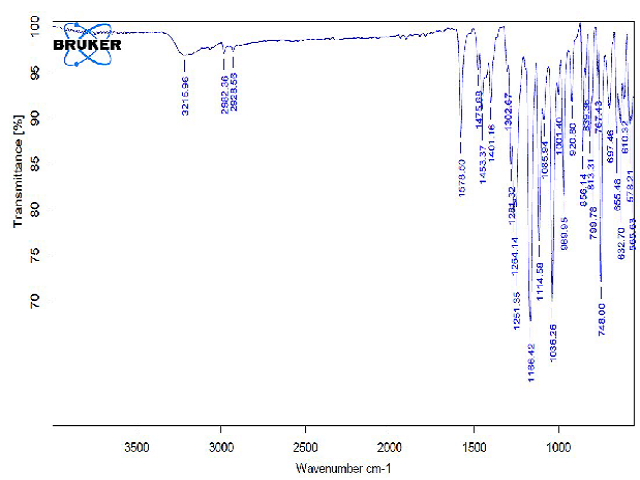
The aim of present research work is to develop a topical gel formulation of Itraconazole loaded nanosponges to increase the solubility, permeability, stability and to control the Itraconazole release for a prolonged period. Itraconazole loaded nanosponges was prepared by cross-linking different concentrations of β- Cyclodextrin with carbonate bonds of di phenyl carbonate in different proportions, which are porous as well as nanosized. Drug was incorporated by solvent evaporation method by dissolving the drug in various solvents like ethanol, acetone and chloroform. The prepared nanosponges were incorporated into carbopol gel. From the encapsulation efficiency of the drug loaded nanosponges formulations, it was observed that as the crosslinking ratio increased the encapsulation efficiency was found to be enhanced. It is also found that the encapsulation efficiency of drug loaded nanosponges were influenced by the solvent used for drug loading by solvent evaporation technique. Based on the drug encapsulation efficiency , drug content and extent of sustained nature , the gel prepared with β- Cyclodextrin and crosslinking agent in 1:1 ratio, chloroform as a solvent and carbopol as a gellling agent (IF12 formulation) was concluded to be the best formulation. All the formulations followed zero order release kinetics and mechanism of drug release was governed by Peppas model.The diffusion exponential coefficient(n) values were found to be in between 0.9402 to 1.1864 indicating non fickian diffusion mechanisam.