Phytochemical Profiling, In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Euphorbia hirta Extracts and In Silico Study Targeting Human Peroxiredoxin 5 Receptor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.3.48Keywords:
Euphorbia hirta, Antioxidant activity, Phytochemicals, human peroxiredoxin5Abstract
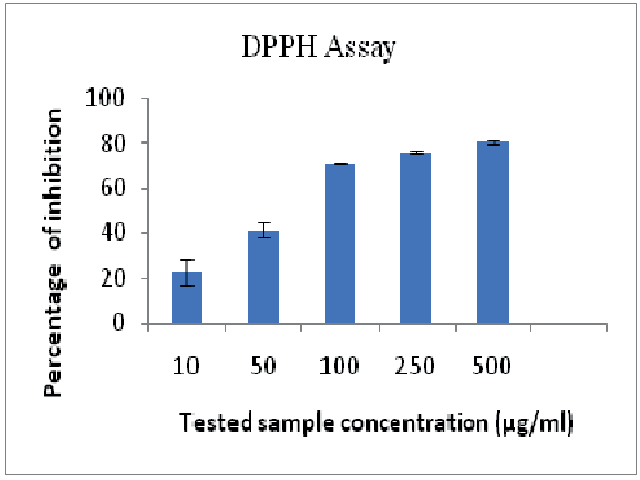
Oxidative stress is responsible for initiation of a variety of health conditions such as diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. Phytochemicals are potential for the oxidative stress management and are alternative to currently used synthetic drugs that cause side effects. The present study was to determine the phytochemicals present in Euphorbia hirta and to evaluate its antioxidant activity. The total phenolic and flavonoid contents, in vitro antioxidant activity (α, α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl free radical scavenging) were evaluated. The phytochemical profile was obtained by GC-MS analysis. The molecular docking was performed to identify the antioxidant activities of major phytochemical constituents against human peroxiredoxin5. The ethanolic extract obtained was rich in phytochemicals with total flavonoids and phenolic acid as 0.18 ±0.009 mg/mg of extract and 0.38 ±0.04 mg/mg of extract respectively. The antioxidant activity was determined with IC50 = 95.1±10 μg/ml. The GCMS analysis identified 33 phytochemicals from the extract. The in silico study resulted in good binding profiles with strongest inhibitory activity to Carpesterol (-8.373Kcal/mol) followed by ethylphenoxybenzene (-8.099 KCal/mol) and tetradecanoic acid ethyl ester (-8.002Kcal/mol). The findings were evaluated on physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties related to ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion) to support the in vitro study. The outcomes may further extended with the toxicity analysis and to the development of therapeutics.