Analysis of Leaf Extract of Zingiber Officinale by a Hybrid Analytical Technique
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.3.45Keywords:
Zingiber officinale, GC-MS, In vitro anti inflammatoryAbstract
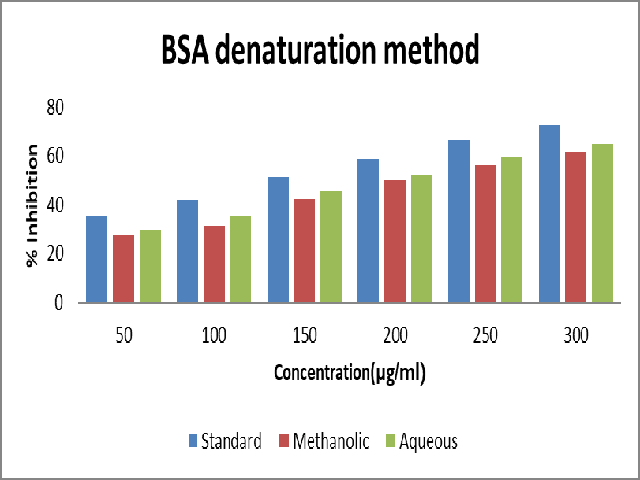
There are number of phytoconstituents present in plants, that have the potential to pre-vent and cure certain human illness. Zingib-er officinalis, a perineal herb used for culinary purposes and alternative medicine is said to possess antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflam-matory, anticancer, antirheumatic, antibacterial and antifungal properties. Though much work has been carried out on the rhizome, there has been limited work done on the leaves of the gin-ger plant. The qualitative phytochemical analy-sis of methanolic and aqueous extract of ginger leaves shows the presence of flavonoids, sapo-nins, phenolic compounds and tannins in meth-anolic and aqueous extract. GC-MS analysis further validates the presence of 13 phytochem-ical constituents such as caryophyllene, phytol, lanosterol, pentadecanoic acid methyl ester and other secondary metabolites in the methanolic extract, and 13 phytochemical constituents in aqueous extract. The leaf extract was screened for Invitro anti-inflammatory activity by inhibition of protein denaturation method and membrane stabilization test. The % inhibition at 300μg/ml of aqueous extract was observed at 64.88%, 66.09% and 50.57% in Bovine Serum Albumin denaturation method, egg albumin denaturation and Haemolytic RBC membrane stabilization method respectively. In case of methanolic ex-tract maximum percentage inhibition was ob-served at 300μg/ml was 61.30%, 63.09% and 46.74% in BSA denaturation method, egg albu-min denaturation and HRBC membrane stabili-zation method respectively.