In Vitro Analysis of Antimicrobial Compounds from Euphorbia milli
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.2s.27Keywords:
Bioactive metabolites, Extraction, Bioactivity, PathogensAbstract
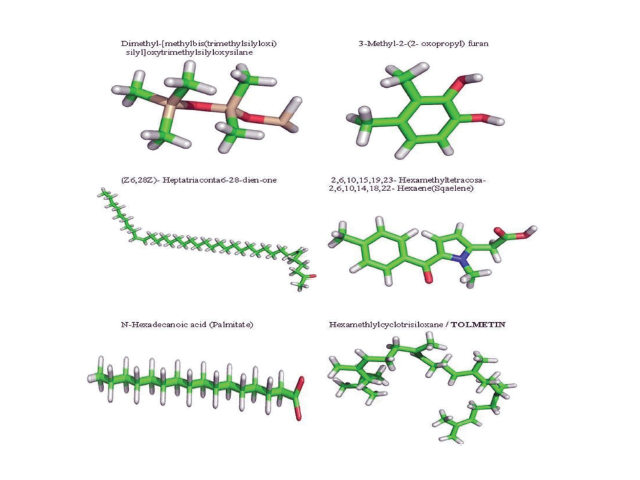
Pharmaceutical and scientific communities are now looking at newer avenues of obtaining antimicrobial agents, and the focus has now been on natural sources. In this study, Euphorbia milli extract was characterised for antimicrobial activity. The antimicrobial effect was determined by calculating minimum inhibitory concentration against the pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumonia, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Shigella dysenteriae. The active metabolites of the plant extract manifested a significant antibacterial effect. In silico analysis was carried out using iGemdock as the docking tool for docking Penicillin Binding proteins against the extracted active metabolites. The docking score Hexamethlyl-cyclotrisiloxane / Tolmetin emerged as the most effective active metabolite against all the pathogens except Shigella dysenteriae N-Hexadecanoic acid was the best choice.