Cloning, Expression, Purification and Contraceptive Efficacy Studies of a GnRH Receptor Based Recombinant Fusion Protein
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.2.15Keywords:
Immunocontraception, vaccines,, Gonadotropin Releasing hormone, Gonadotropin Releasing hormone receptor, stray dog populationIntroductionAnAbstract
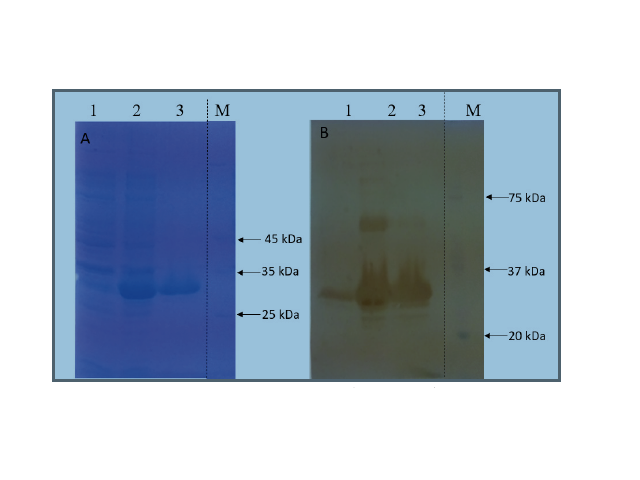
The need for a contraceptive vaccine to control stray dog population is very essential in the current scenariowith increasing incidence of rabies and dog bites. It is seen as a viable non-surgical alternatemethod to spaying and castration.In the present study, a recombinant protein comprising of Gonadotropin Releasing hormone (GnRH) and Gonadotropin Releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR) were assembled along with the T cell epitopes of tetanus toxoid and canine distemper virus and was studied to explore its potential in contraception. The GnRH and GnRH receptor genes were successfully cloned into pET28a vector and expressed in BL21 DE3 bacterial expression system and further purified using Ni-NTA purification system.The resultant recombinant protein was expressed in E. coli to give rise to a 30kDa fusion protein. Further confirmation of the recombinant protein was done by western blot using Anti-His antibody. The mice were immunized with the GVAC09 fusion protein along with Freunds adjuvant. ELISA studies revealed the generation of a high antibody titre against the immunogen. In vivo contraceptive studies oftheGVAC09 immunized mice led to a decrease in litter size. From the current study with the proven immunocontraceptive potential of the recombinant protein, with further improvements GVAC09 recombinant protein has the potential to be a viable contraceptive vaccine to control stray dog population.