Biosynthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles from Annona muricata Fruit Aqueous Extract and Investigation of their Antioxidant and Antimicrobial potentials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.1.10Keywords:
Annona muricata, Green synthesis, Selenium nanoparticles, Antioxidant activity, Antimicrobial activityAbstract
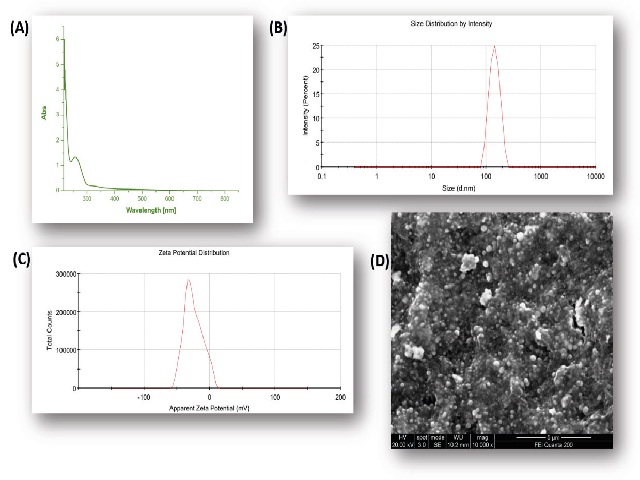
The focus of the research was to synthesize biogenic selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) from A. muricata in an environmentally friendly, non-toxic, biocompatible, and affordable way. The successful synthesis of SeNPs was preliminarily confirmed by the development of brick-red color. The DLS pattern in our investigation revealed that the synthesized SeNPs were nanosized, with sizes ranging from 80 to 120 nm. The zeta potential for SeNPs was found to be -26 mV and indicated that SeNPs were negatively charged. The micromorphology of SeNPs was determined by SEM analysis and found that they were spherical in shape and size of 120 – 160 nm. EDX showed that SeNPs contain selenium (86.22%), carbon (7.30%), and oxygen (3.51%). In antioxidant activity, IC50 values of SeNPs were determined as 58.98 ± 0.70 and 66.10 ± 1.01 μg/mL in DPPH free radical scavenging and ABTS free radical scavenging activities, respectively. In antibacterial activity, SeNPs exhibited potential antibacterial activity by the zone of inhibition assay. The strong antimicrobial activity of SeNPs was observed against Gram-positive bacteria related to Gram-negative bacteria. In the microwell dilution technique, MIC and MBC of SeNPs were found best against Gram-positive bacteria related to Gram-negative bacteria. The assynthesized SeNPs could be highly beneficial as antioxidant and antibacterial agent in the biomedical field.