Phytochemical, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Analysis of Indigenously used Folk Medicinal Plant Ixora notoniana Wall.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.1.7Keywords:
Paliyar Tribal, Ixora notoniana, antioxidant, antimicrobial activities, methanolAbstract
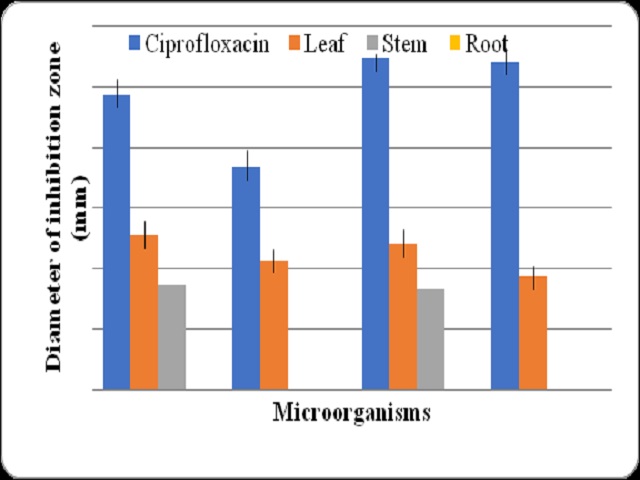
Ixora notoniana plant parts are traditionally used by Paliyars, who are indigenous tribal group of Tamil Nadu state of India, to treat various disorders such as tooth ache, skin and stomach problems. The present investigation aimed to search for an alternative antibiotic and antioxidant from traditionally used medicinal plant and to give ethnopharmacological evidence for its traditional usage. Phytochemical screening, antioxidant and antimicrobial studies were conducted with leaf, stem and root extracts. Methanol was used as solvent for the extraction process owing to its high extraction power and polarity. Preliminary phytochemical analysis with the extracts confirmed the presence of alkaloid, phenol, flavonoid and saponin in the extracts. Four bacterial species (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis) and a fungal species (Trychopyton simii) were used for the evaluation of antimicrobial activities of the selected plant extracts using disc diffusion method. In antimicrobial studies, leaf extract exhibited antimicrobial activities against all the tested microorganisms in the range between 9.33 mm and 13 mm of inhibition zone, whereas the stem extract showed activities against E. coli, S.aureus and T. simii only. All the plant extracts were exhibited noticeable and dose dependent antioxidant activities in both DPPH and FRAP assays. Highest antioxidant activities were observed in leaf extract (43.91%) at 200 μg/ml concentration, root extract showed lowest activity (5.45%) at 25 μg/ml concentration. Oxidative stress is one of the instrumental factor in the stomach disorder and tooth and skin problems are associated with the bacteria and fungi.The present study observe the both antioxidant and antimicrobial activities in the extracts, hence the usage of plant as a remedy for stomach, tooth and skin problems could be justified.