In silico Evaluation of 2,4-diaminoquinazoline Derivatives as Possible Anticancer agents
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2022.1.2Keywords:
Quinazoline, In silico, Caspase-9, Drug-likeness, AnticancerAbstract
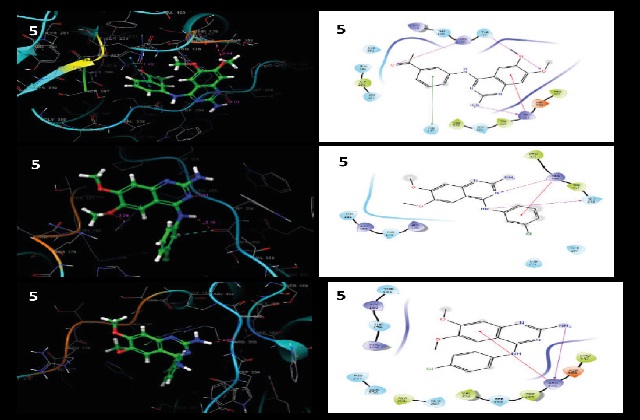
The quinazoline nucleus is one of the most privileged scaffolds for the designing of pharmacodynamic compounds. There were several molecules originated from natural as well as synthetic sources. Molecules with a quinazoline nucleus have been found not only as potential anticancer agents but also for treating other diseases. In the present study, the designed compounds were subjected to in silico screening followed by molecular docking with caspase-9 protein. Initially, compounds were screened for drug-likeness using Swiss ADME, Osiris Property Explorer, ProTox-II, and PASS web servers. It has been found that most of the compounds interact with caspase-9 through H-bonding. During the preliminary screening, the compounds have shown drug likeness and devoid of any mutagenicity and hepatotoxicity. Our results indicate that these scaffolds could be further improved for their anticancer efficacy by structural modifications.