Effect of Natural Compounds on Glioblastoma Multiforme Pathways
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2021.6.5Keywords:
Bromelain, Cytoscape, Epigallocatechin 3 Gallate, Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase- ERBB4, Signalling pathway, Temozolomide, Tumor MicroenvironmentAbstract
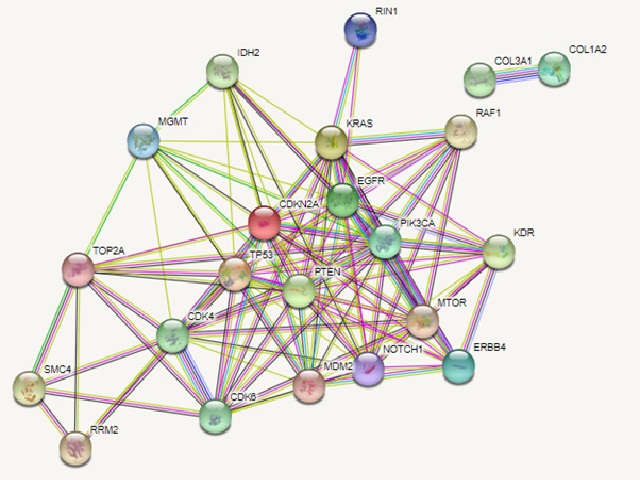
Glioblastoma is one of the most debilitating forms of brain tumour. It accounts for 17% of all the brain tumours and has resulted in 251,329 deaths in 2020 itself. Several studies performed on patient profiling have revealed that many genes tend to be overexpressed or mutated in many GBM patients and hamper the signalling and growth pathways. Additionally, there is a requirement to explore supplementary or alternative treatment that can aid in overcoming the resistance caused by standard care treatment (Temozolomide with radiation). The preliminary analysis on inhibitory potential of certain phytocompounds on the crucial genes involved in GBM has been studied in silico. The network of the genes critical for GBM has been analysed through several plugins of Cytoscape software like BiNGO and MCODE based on factors such as degree, closeness and betweenness. The network analysis gave out a cluster of 97 interactions with 16 interacting proteins. ERBB4 emerged as the seed protein indicating its crucial role in pathways. The BiNGO plugin gave out the gene ontology data describing the functions of the genes of the cluster. Additionally, the properties of ligands were studied by the PharmaGist server and 3D patterns of shared features by all or most input ligands of selected phytocompound were analysed and aligned. Upon docking the seed protein (ERBB4) individually with the best combination of aligned ligands yielded bromelain and EGCG as the compounds with best binding affinity of -9.8 and -9.2 kcal/mol respectively. This study has provided an important lead for further in vitro study to analyse the effect of combination of phytocompounds on the critical signalling pathways of GBM.