In Silico Elucidation of Antineoplastic Mechanisms in Cucurbita pepo Seed Extract Using Advanced Molecular Modeling Techniques
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.4s.4Keywords:
Cucurbita pepo, HER2, Cancer, Phytochemicals, Nutrition, Molecular Docking, SimulationAbstract
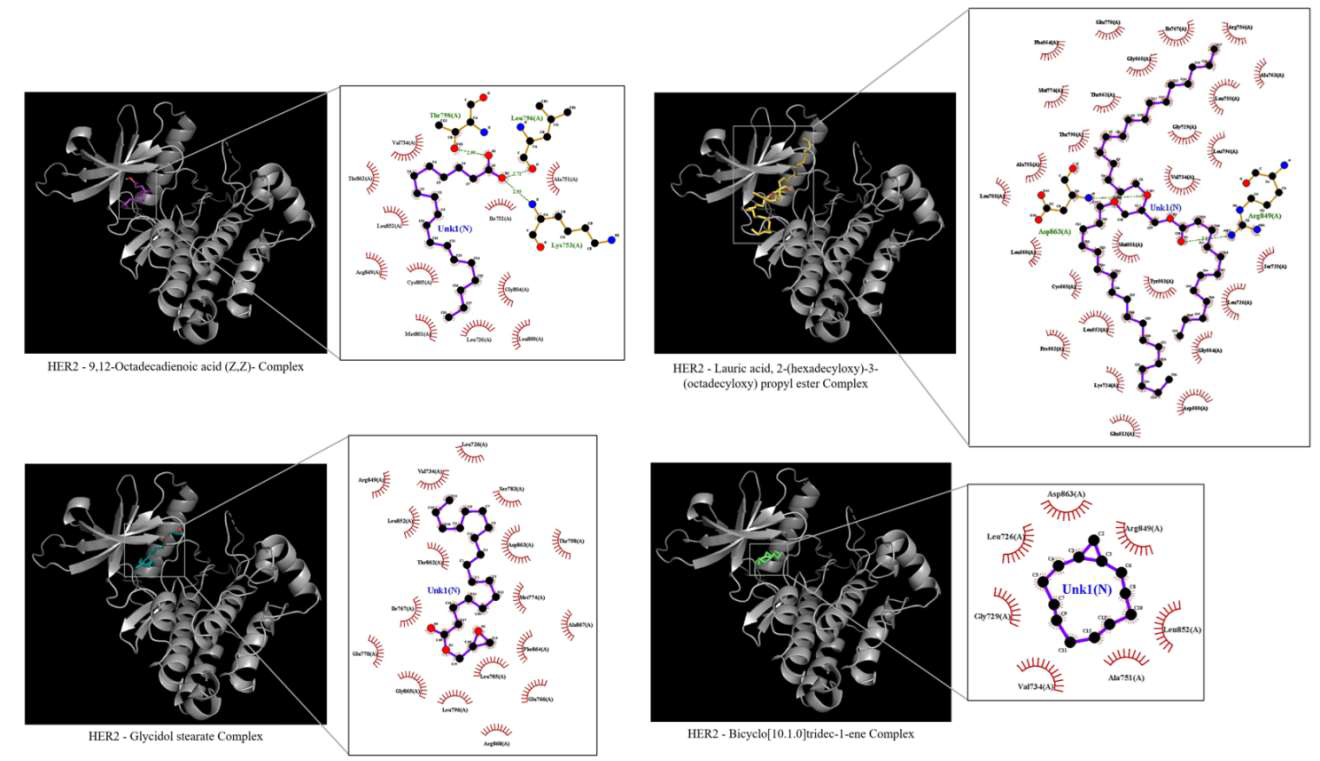
Cancer continues to pose a significant global health burden, with lung and breast cancer among the most frequently diagnosed types. In this study, the most nutrition-rich andanticancer potential of Cucurbita pepo (pumpkin) seed extract was investigated using an integrative computational biology approach. Bioactive constituents from the aqueous extract were identified through Gas Chromatography- Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis. Molecular docking studies, conducted using PyRx, evaluated the binding affinity of these phytochemicals toward the HER2 (PDB ID: 3PP0) receptor, a critical target in cancer therapeutics. Notably, Stearic acid glycidyl ester, Linoleic acid, and Trilinolein demonstrated strong binding interactions with HER2, suggesting their role in modulating oncogenic pathways. Drug-likeness and pharmacokinetic parameters were assessed via ADMET analysis, confirming favorable bioavailability and toxicity profiles. The most promising compound-receptor complex was further validated through a 100-nanosecond molecular dynamics simulation, which revealed sustained structural stability. These findings propose C. pepo as a promising natural source of anticancer agents andprovide a strong basis for future in-vitro and in-vivo experimental validation.