Essential Metals (Calcium and Znic) and Chelating Agent (Monoisoamyl 2, 3-dimercaptosuccinic acid) Attenuates Arsenic Induced Neurochemical Alterations in Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2021.4.37Keywords:
Arsenic developmental toxicity,, Essential metals, MiADMSA, Brain regionsAbstract
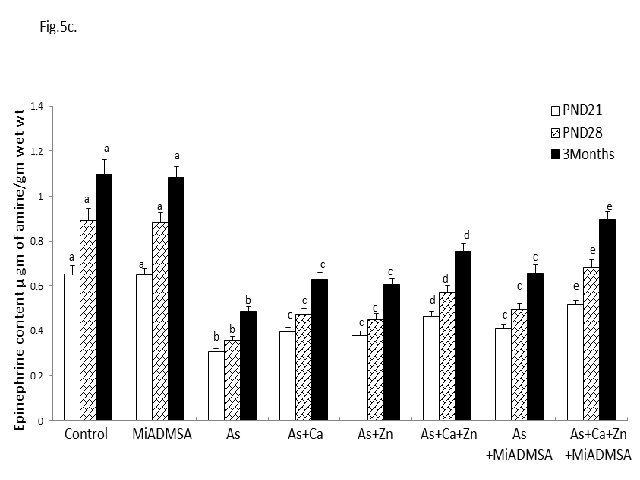
Arsenic (As) is ubiquitous in environment and well known developmental neurotoxicant. In the present study we examined the protective effect of calcium (Ca), zinc (Zn) and monoisoamyldimercaptosuccinic acid (MiADMSA), either individually or in combination against As induced alterations in catecholamine levels, acetylcholine (ACh), acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) and monoamine oxidase (MAO) in brain regions (cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum) of PND 21, PND 28 and 3 month old rats. Gestational and lactational (GD6 to PND 21) As exposure significantly decreased the levels of catecholamines (dopamine, epinephrine and nor epinephrine), AChE and MAO activities with an increase in ACh content in all selected age points. The observed alterations in these neurochemcical parameters were higher at PND 28. Among the brain regions, As induced alterations in catecholamines levels and cholinergic system were more pronounced in hippocampus than cortex and cerebellum. Individual supplementation of essential metals (Ca or Zn) or chelating agent (MiADMSA) significantly reversed the As induced neurochemical alterations. However, combined supplementation of essential metals with the chelating agent produced greater reversal effects in reducing As induced neurotoxicity.