Formulation and evaluation of amoxicillin trihydrate oral lozenges for treating upper respiratory tract infections
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2021.1.7Keywords:
Amoxicillin Trihydrate, Ginger, Tulsi, PEG 4000, MCC, SteviaAbstract
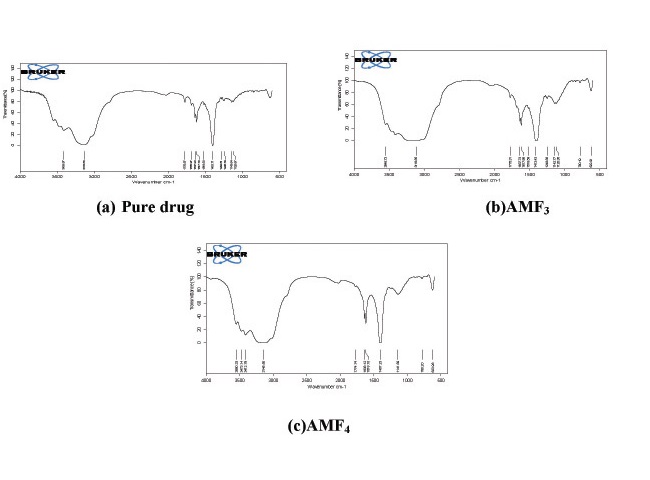
In the present investigation an attempt has been made to develop Amoxicillin Trihydrate oral lozenges in treatment of upper respiratory tract infection. The lozenges were formulated by soft lozenges method employing Amoxicillin Trihydrate alone and in combination with natural antiseptic ingredients. The lozenges were prepared employing PEG 4000 as matrix base, Stevia (natural sweetener), Acacia (polymer), MCC (disintegrate) other excipients. The prepared medicated lozenges were characterized for Weight uniformity, hardness, Drug content, and dissolution by standard pharmacopeia methods. The results of the evaluation tests obtained were within the limits. Formulations were tested for drug Excipient interactions by FTIR spectral analysis. The results revealed that there were no major interactions between the drug and polymers used for the preparation of lozenges. Antimicrobial activity studies were performed for different lozenges formulations. AMF2 formulation showed greater Zone of inhibition. This may be due to synergistic antimicrobial effect of Amoxicillin Trihydrate, Tulsi and Ginger. Accelerated stability studies were conducted as per ICH guidelines and found that there wasn’t any substantial change in the prepared formulations