Screening and Purification of L-asparaginase Production by Aspergillus quadrilineatus Using Agro Wastes and Vegetable Peels
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.2.19Keywords:
Fungi, Vegetables, L-asparaginase, Aspergillus quadrilineatus, papaya peels, RhizosphereAbstract
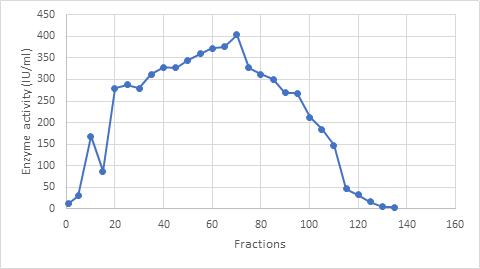
Enzymes are the name for the biocatalysts that are created by living cells. These are intricate protein molecules that start chemical reactions essential to life. They are colloidal, thermolabile, and have a particular action. L-asparaginase (also called L-asparagine amido hydrolase, E.C.3.5.1.1) is an extracellular enzyme that has attracted a lot of attention since it is used as an anticancer drug. To assess the growth capacity of the selected fungus Aspergillus quadrilineatus, a preliminary experiment was carried out using vegetable peels and agricultural waste as substrate. The by-products that were utilized included wheat bran, cornmeal, gram flour, wheat flour, rice flour, rice husk, and peels from green peas, onions, carrots, and papayas. On the other hand, papaya peel medium worked well as a source of media for improving growth in Aspergillus species. This work focuses on the purification, mass-scale production, screening, and characterization of the Fusarium proliferative-derived L-asparaginase enzyme. The crude enzyme was removed, followed by precipitation with ammonium sulphate, filtration over a Sephadex column, and ion exchange chromatography to further purify the L-Asparaginase. The reaction of the enzyme to different temperatures, pH values, substrate concentrations, and incubation times was evaluated in order to define it. Because it can catalyze the conversion of l-asparagine to l-aspartic acid and ammonia, l-asparaginase is one such crucial enzyme that has found commercial usage in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Although l-asparaginase may be produced by a variety of bacterial and fungal sources, researchers are particularly interested in how these organisms might generate the enzyme commercially utilizing less expensive substrates.