Optimizing Formulation and Economic Evaluation of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria for Enhanced Cauliflower Growth and Yield
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.2.18Keywords:
Agricultural, Cauliflower Growth, Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria, Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria, Rhizosphere, Ellman’s assayAbstract
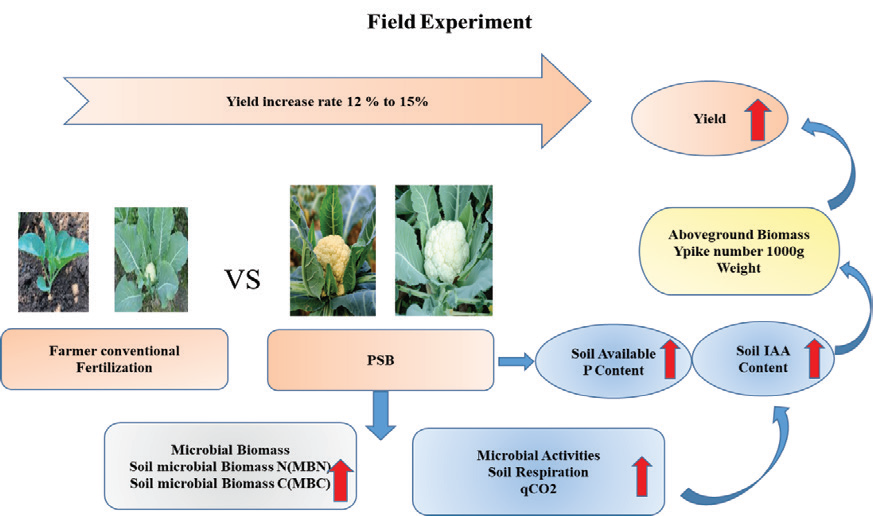
A shortage of phosphorus (P), a necessary mineral ingredient for agriculture, may result in lower grain quality, productivity, and growth in cereal crops. Much of the phosphorus that is sprayed in agricultural contexts is immobilized in the soil, which limits the amount of phosphorus that is available to plants. This study focused on investigating the microbial communities in the rhizosphere of cauliflower crops from Kanpur, Unnao, and Lucknow districts in India, known for their fertile soils and favorable agricultural conditions. Soil samples were collected and screened for phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. PSB was isolated using Pikovskaya’s agar medium, and nitrogen-fixing bacteria were identified through nitrogen-free media supplemented with a bromothymol blue indicator. Morphological, biochemical, and molecular techniques were employed for characterization. The isolated strains were then tested for their impact on cauliflower growth and yield parameters under controlled conditions. Results showed significant enhancements in plant growth and yield parameters, suggesting potential applications in agricultural practices.