In vitro Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Selected Sri Lankan Medicinal Plants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.2.17Keywords:
Acetylcholinesterase, Wrightia antidysenterica, Flueggea leucopyrus, Ellman’s assayAbstract
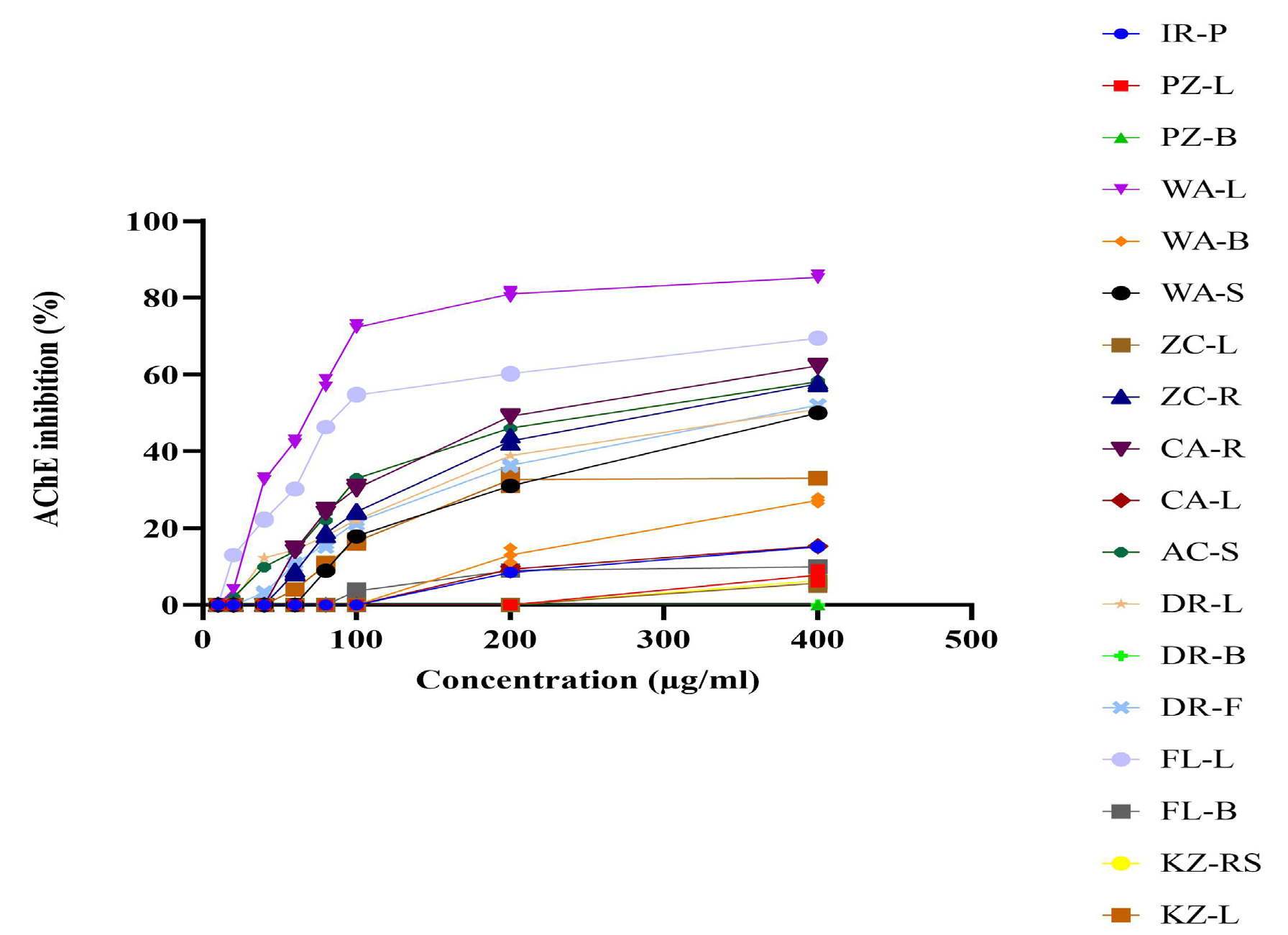
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition is a well-accepted therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease and many categories of dementia. Medicinal plants are promising sources of useful AChE inhibitors and have been used to treat Alzheimer’s disease by people around the world. This investigation was carried out to assess the AChE inhibitory activities of the crude organic extracts of nine Sri Lankan medicinal plants. Air dried, powdered samples of different plant parts were sequentially extracted with 3 organic solvents to yield a total extract of the individual plant part. These extracts were tested for AChE inhibitory activity using Ellman’s assay in 96-well microplates. Galantamine (IC50 1.57 ±0.01 μg/ml) was used as the standard acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and all the tests were done in triplicates. Potent AChE inhibitory activities were shown by the leaf extracts of Wrightia antidysenterica and Flueggea leucopyrus with IC50 values of 64±0.5 μg/ml and 107±0.1 μg/ml, respectively. Furthermore, Zingiber cylindricum rhizome extract and Areca concinna seed extract also exhibited considerable AChE inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 189±1.4 μg/ml and 217±1.2 μg/ml, respectively. Hence, it can be concluded that W. antidysenterica and F. leucopyrus possess potent anti-cholinesterase activity and can be used to isolate drug leads with anti-acetylcholinesterase activity.