Photosynthetic Based Technology For The Bioremediation Of Domestic Sewage Water Using Anoxygenic Bacteria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2021.3s.28Keywords:
Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria, Bioremediation, Pollutant, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Sewage waterAbstract
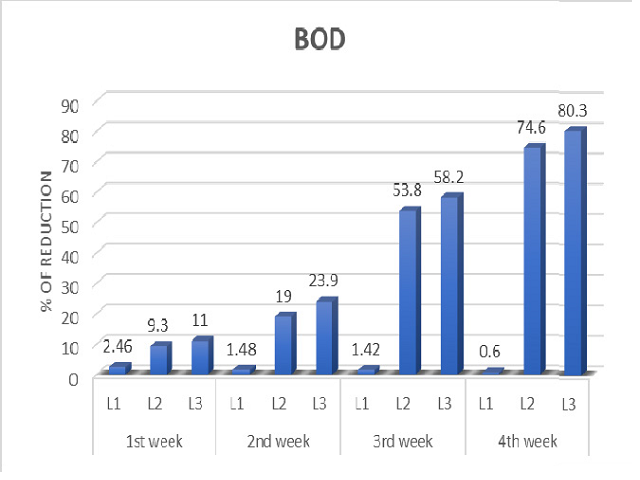
Bioremediation employs the use of naturally occurring organisms to break down hazardous substances into less toxic or non-toxic substances. The conventional treatment method of domestic sewage water is expensive and generates waste sludge that requires further handling and the problem of disposal of sludge into the environment is risky as it has a high potential to pollute the environment. The development of a simple and cost effective process allows the implementation of bioremediation in a safer and effortless manner. Therefore in this investigation microbiological and chemical analyses were very useful to suggest the best ways to improve bioremediation limits in domestic sewage water. In the study indigenous anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria were isolated from domestic sewage water to treat domestic sewage waste water, to develop a costeffective process for bioremediation. Domestic sewage water was analyzed for different physico-chemical parameters such as pH, Temperature, TDS, TSS, TS, DO, BOD, COD, total sulphate and chlorides using bio inoculants of anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria isolated and domestic sewage water in an suitable light, pH and temperature conditions. The results showed that among the 3 anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria isolated; isolate RP2 (Rhodopseudomonas palustris) could grow well at pH 8, temperature 30°C and also reduce more pollutant parameters in domestic sewage water during bioremediation in the period of four consecutive weeks at the rate of 80%.