The Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled trials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.1.10Keywords:
Parkinson’s disease, ursodeoxycholic acid, meta-analysis, ATP concentrationAbstract
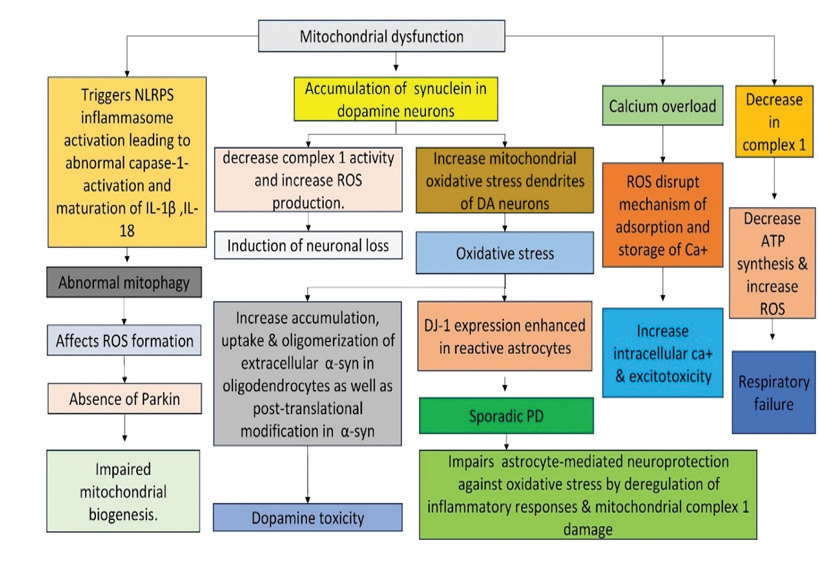
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive degenerative disorder involving dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Along with motor activity impairment, PD patients also have a range of neuropsychiatric, cognitive, and autonomic problems. Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) has been used to treat a wide range of liver-related ailments, including gallstones, cholestatic diseases, and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). In addition to this, randomised control trials on the effects of Parkinson’s disease have been conducted on UDCA. In the present study, we validate the effect of UDCA on Parkinson disease using meta-analysis. Various electronic databases such as Web of Science, PubMed/ Medline, Cochrane library and Scopus were used for search of articles. The randomized control trials (RCTs) for the effect of interventions of UDCA on Parkinson disease was evaluated using meta-analysis (Review Manager 5.4) software. A total of 304 articles were identified, of which 3 met the inclusion criteria. When compared to patients receiving the control medication, the UDCA-treated patients had higher concentrations of inorganic phosphate (Pi) and ATP. The z scores of UDCA on Pi and ATP concentration were determined to be 0.08 and 0.71 with p-values of 0.00001 and 0.0001, respectively. UDCA might increase brain mitochondrial activity and cellular ATP availability and could possibly have therapeutic disease-modifying effects. Ursodeoxycholic acid administrations in PD significantly increase the concentration of Pi and ATP and maintain ATP homeostasis by increasing ATPase activity and ATP production.