A Study on Toxicity Mechanisms of Xenobiotics Using Network Pharmacology Approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.4s.11Keywords:
Xenobiotics, Network pharmacology, PubChem, PANTHER pathway, PharmMapperAbstract
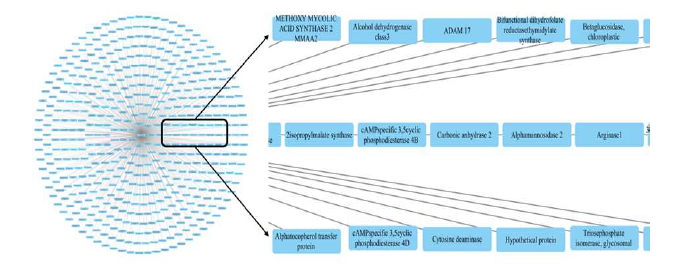
In recent years, modern medicine has grown exponentially. Many drugs are being developed and reused for different diseases. Although these drugs help cure these diseases, there are some side effects on the human body. The most affected organ in the human body. Is the liver these side effects in the liver were studied using marine toxicity studies using several species of marine organisms. This study aimed to investigate the toxicity mechanisms of xenobiotics using a network pharmacological approach. Xenobiotics are chemicals that are foreign to an organism and exposure to them can cause adverse health effects. Network pharmacology is a systems-level approach that integrates information about interactions between drugs, proteins, and biological pathways. The study involved using publicly available data to construct a human xenobiotic-protein interaction network using sites such as PubChem, PharmMapper, the KEGG/PANTHER pathway, and the Cytoscape software. The network was analysed to identify key proteins and pathways involved in xenobiotic toxicity. The study also explores the potential for repurposing existing drugs to minimize xenobiotic toxicity. Study results reveal several key targets and pathways involved in xenobiotic toxicity, including oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. The study also identified several existing drugs that could potentially be repurposed to minimize xenobiotic toxicity. Taken together, this study provides insight into the mechanisms underlying xenobiotictoxicity and highlights the potential for using network pharmacological approaches toidentify novel therapies for the treatment of xenobiotic diseases.