Antibiofilm activity of ethanolic root extract of Vetiveria zizanioides against dental pathogens
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.4s.8Keywords:
Vetiveria zizanioides, anti-biofilm, antimicrobial, antioxidant and antiinflammatoryAbstract
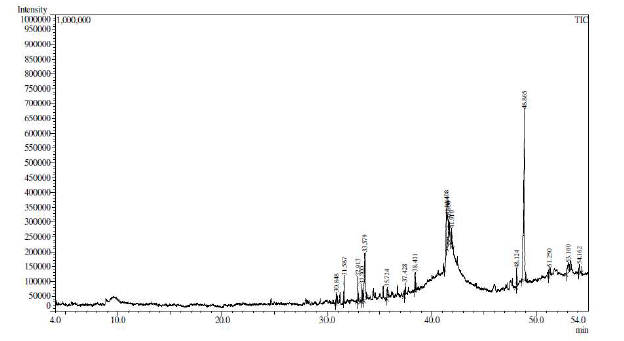
Biofilm infections, shielded from antibiotics and immune defences, pose a major health threat. Plants offer potential solutions due to their diverse bioactive compounds. This study investigated the root extract of Vetiveria zizanioides for its composition and tested for its ability to inhibit biofilms, fight bacteria and fungi, reduce inflammation, and combat oxidative stress in pathogens. The anti-biofilm properties were assessed using test tube method and a crystal violet assay. Phytochemical composition was analysed via Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GCMS). Antimicrobial activity was tested against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumonia and Candida albicans using both agar well plate and micro broth dilution methods. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects were determined by DPPH and protein denaturation assays, respectively. The ethanolic extract contained 17 identified compounds, primarily sesquiterpenes and fatty acids. Major compounds were identified as 17-hydroxy-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4,ol, z,z- 8,10-hexadecadien-1-ol, formic acid, campesterol, cedren-13-ol, It inhibited biofilm formation in various pathogens, with the strongest effect against Staphylococcus aureus (75%) and the weakest against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (25%). The extract also displayed antimicrobial activity against all tested bacteria and fungi, with the best activity against Staphylococcus aureus (23mm inhibition zone). Additionally, it exhibited dose-dependent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These findings suggest Vetiveria zizanioides extract has significant potential for combating biofilmrelated infections. Future research should focus on isolating and purifying active compounds, assessing their safety and longterm effects, and exploring their potential as therapeutic agents.