Exploring Molecular Interactions and Pathways in Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): A Comparative Analysis of Patients With and Without Anxiety
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.4s.5Keywords:
MDD, DEG’s, Biomarkers, Pathways, Therapeutic targetsAbstract
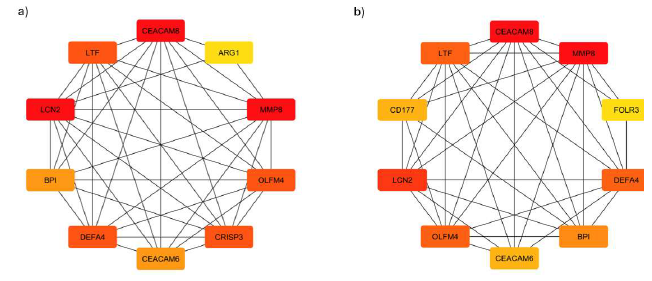
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) presents as an intricate mental health issue often associated with Anxiety. In this study, we used data from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) to investigate how anxiety acts as a comorbidity to MDD at the molecular level. We used NCBI GEO Accession ID: GSE98793 for this study. This microarray dataset examines the gene expression profiles associated with MDD both with and without anxiety. As the outcome of the study, a total of 15 significantly upregulated Differential Expressed Genes (DEGs), 4 significantly down regulated Differential Expressed Genes (DEGs) were found in MDD with anxiety data’s and 5 significantly upregulated Differential Expressed Genes (DEGs), 18 significantly down regulated Differential Expressed Genes (DEGs) were found in MDD without anxiety data were obtained from the dataset. After protein-protein interaction networks were generated using STRING DB, the molecular associations for MDD were visualised using Cytohubba, a Cytoscape plugin. We performed a functional enrichment analysis using the DAVID Functional Annotation tool to identify the biological processes and pathways associated with the up-regulated and downregulated genes in the anxiety and nonanxiety groups. ARG1, CRISP3, DEFA4, LCN2, BPI, and LTF were discovered in the anxiety group, while HLA-DQB1, FAM3B, GATB, and HLA-DQA1 were discovered in the non-anxiety group. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway and Gene Ontology (GO) were used to analyse differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Interestingly, factors like Staphylococcus aureus infection, the intestinal immune network's role in producing IgA, the steps involved in processing and presenting antigens, and the development of Th1 and Th2 cells are all processes that play a role in the illness and its comorbidity.