Mutational Stability Profiling and Functional Analysis of Spike Protein In Indian Sars Cov-2 Delta Variants: An In Silico Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.4s.4Keywords:
SARS CoV-2, Spike protein, Mutation, CoronavirusesAbstract
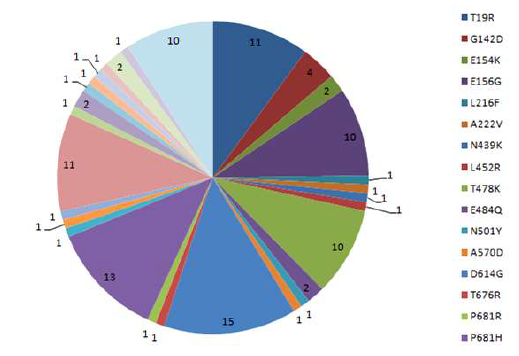
Amidst the global pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, researchers are actively studying its evolution and impact. This research delves into the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant, using advanced computational methods to analyze mutations and their effects. By examining mutations and their evolutionary connections in the spike protein using data from databases, the study aims to gain insights into the virus's behavior.To gauge the stability of the spike protein variants, we used various methods. We predicted protein sequence disorders using PONDR. We also used the I-Mutant v2.0 bioinformatics tool to assess how mutations affected stability. We then performed functional studies using Protparam and NetPhos to analyze the consequences of these mutations. These analyses identified several key mutations in the spike protein, especially the D614G substitution. This polar-to-nonpolar amino acid change was particularly noteworthy.Our research identified significant mutations in the spike protein of the Delta Indian variant of SARS-CoV-2, including: T19R, E156G, L452R, T478K, P681R, and D950N. Deletions occurred at positions Y145, F157, and R158. Analysis showed increased phosphorylation of the spike protein, hinting at potential regulation by these mutations. Using structural modeling by Spdbv tool, we found that mutations within the Receptor- Binding Domain (RBD) region reduced protein stability. This study enhances our understanding of the mutations and their impact on the function of the Delta Indian variant's spike protein. Our research explores how mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus affect how its proteins work and stay stable. By understanding these effects, we can lay the foundation for future studies that design treatments specifically for new SARS-CoV-2 variants. In summary, our work shows that SARS-CoV-2 is constantly evolving, making it crucial to keep track of changes and keep researching to help guide health policies.