Utilizing OncomiR and TSmiR as Biomarkers for Screening Breast Cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.4s.2Keywords:
Breast Cancer, Functional Enrichment, Oncomir, TS Mir, PPI NetworkAbstract
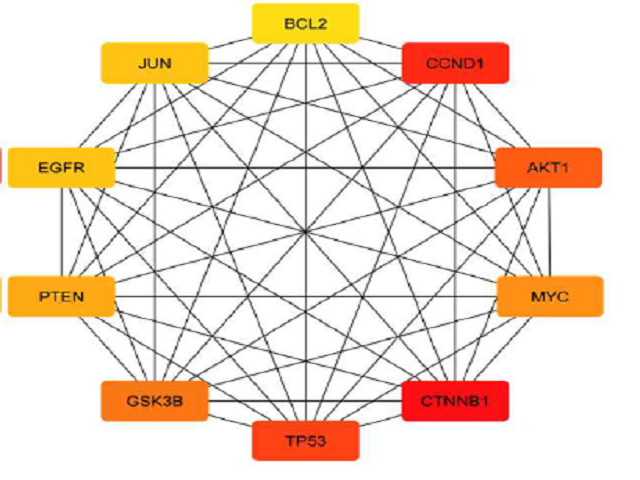
Breast cancer stands out as a significant threat to women globally, emphasizing the urgent need for reliable diagnostic and prognostic markers.Numerous studies have shown that miRNAs assist as either an oncogene or tumor suppressor. As a result, they are recognized as non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting cancer outcomes.Through an in-depth literature review, we have identified numerous upregulated miRNAs, including miR-9, miR-10b, miR-21, miR-29a, miR-92a, miR-148a-3p, miR-155, miR-221, miR-222, and miR-373. Conversely, we have identified downregulated miRNAs, including miR-34a, miR-96, miR-99a, miR-125b, miR-145, miR-200c, miR-203, miR-214, miR-411, and miR-486.We used the miRWalk database to predict target genes associated with each miRNA and constructed a comprehensive network. Additionally, gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were conducted to delve deeper into the functional significance and molecular pathways associated with the identified miRNAs target genes. Additionally, we constructed a Protein-Protein interaction networkbased on the miRNA-target genes.Further analysis was directed towards the target genes of OncomiRs (EGFR, MYC, CTNNBI, TP53, CCDNDI, BCL2) and TSmiRs (TP53, CTNNBI, AKT1), exploring their involvement in signaling pathways.This study delves into the utilization of miRNA for the early screening and monitoring of breast cancer.