BCL Protein and It’s Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway: A Literature Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.4.52Keywords:
BCL-2 proteins, BH3 only proteins, anti-apoptotic proteins, pro-apoptotic proteinsAbstract
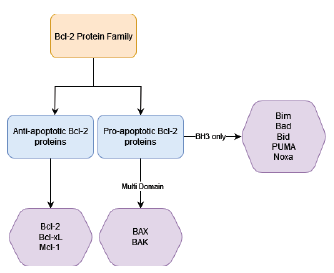
The BCL (B-cell lymphoma) protein family is a diverse group of regulators critically involved in apoptosis, a tightly controlled process crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis. Dysregulation of apoptosis is a common feature in cancer, emphasizing the need to comprehend the intricate mechanisms underlying the function of the BCL family. This literature review offers a comprehensive exploration of the structural domain organization of the BCL family, shedding light on how these proteins orchestrate apoptosis. The family comprises anti-apoptotic proteins, pro-apoptotic effectors, and BH3(BCL- 2 homology 3)-only proteins, each with distinct structural features and functional roles in apoptotic signaling pathways. Anti-apoptotic proteins like BCL-2 serve as guardians against cell death by preserving mitochondrial integrity. Pro-apoptotic effectors, on the other hand, actively promote apoptosis by inducing mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. BH3-only proteins act as molecular switches, mediating the delicate balance between proand anti-apoptotic signals. This review delves into the specific role of BCL-2, a prominent family member, in various cancers such as lung, breast, and prostate cancers. Highlighting its significance as a potential therapeutic target, the article underscores the importance of understanding the molecular nuances of BCL-2 in cancer progression. Moreover, recent advancements in BCL-2 inhibitor development are discussed, showcasing their potential as targeted therapies for cancer treatment. These inhibitors represent a promising avenue for personalized cancer therapy, aiming to selectively induce apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing normal cells. The review emphasizes the importance of these inhibitors in addressing the specific challenges posed by BCL-2 dysregulation in diverse cancer types. By elucidating the structural and functional aspects of the BCL protein family, this literature review provides valuable insights into apoptotic signaling pathways. It not only deepens our understanding of the molecular intricacies governing cell death but also presents novel strategies to modulate apoptosis in cancer cells. Ultimately, the article highlights the significance of BCL proteins as promising therapeutic targets and the potential of BCL-2 inhibitors for personalized cancer therapy, paving the way for advancements in cancer treatment.