Development of point-of-care lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for foot and mouth disease diagnosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2021.1.2Keywords:
Foot and Mouth Disease, Sensitivity, Specificity, Lateral Flow Assay, ELISA, Point-of- CareAbstract
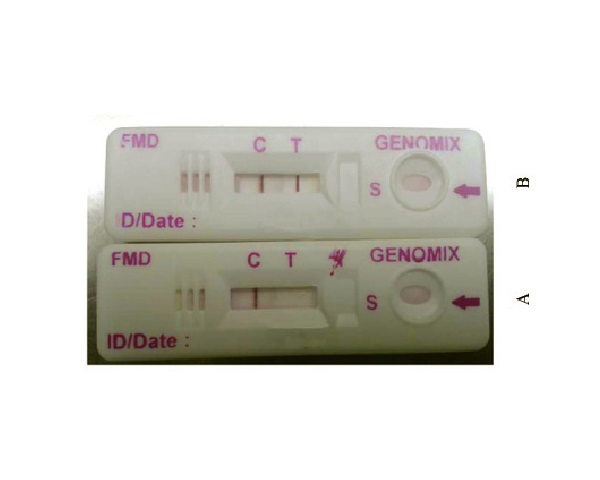
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is highly infectious, contractable disease of ungulates and is associated with cattle which causes high economic losses in livestock industry. Virtual control of FMD requires specific and sensitive point-of-care diagnostic tools to eradicate the disease spreading. So far, the diagnostic tools used for Foot and Mouth Disease Virus (FMDV) are molecular based assays which are more expensive. The main objective of this research study is to develop and evaluate point-of-care test for rapid detection of FMDV in animals. For this study, a highly specific and sensitive FMD nonstructural protein (NSP) antibody rapid immunodiagnostic assay was developed using recombinant 3ABC (r3ABC) protein of FMDV for the detection of antibodies against FMDV and compared with commercial ELISA. The FMDV 3ABC gene was cloned into pET28a (+) vector and the gene product was expressed in E. coli BL21 cells. The expressed r3ABC protein was detected by SDS-PAGE analysis which resulted in a protein band with approximate molecular weight of 60 kDa. Purified r3ABC antigen was used as a detection reagent in rapid Lateral Flow assay (LFA). The diagnostic Assay was performed with 33 reference and 380 field samples and results showed that 94% sensitivity and 98.9% specificity. This study revealed that successful expression of 3ABC gene and diagnostic assay development lead to the identification of diseased animals. It further demonstrated that LFA as potential diagnostic tool for the point-of-care diagnosis of FMDV in large herds within limited time.