Development of Biodegradable Tapioca Starch Films Incorporating Green Synthesized Zinc oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Preservation and Packaging of Sweet lime Segments: A Study of Their Physical and Antimicrobial Properties
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.3s.20Keywords:
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle, Tapioca Starch, Green Synthesis, Sweet Lime SegmentsAbstract
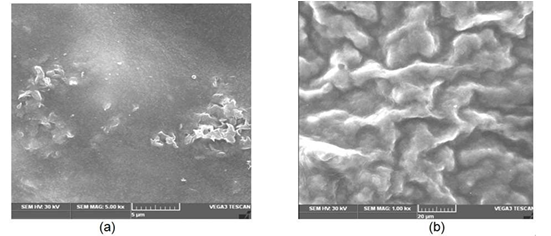
ct Packaging has been on the environmental agenda for decades. It has been discussed and debated within the society as an environmental problem and the focus has been on the packaging material, including recycling options.In this research workgreen synthesized zinc oxide index (27.02%±0.35) & solubility (20.70%±0.74), was fine, flexible, and had better transparency.Film F2 also proved to have a significant antimicrobial activity. Thus, from the overall results tapioca starch film F2 was found to be the better option for food packaging applications when comparedtoF1 film. nanoparticle was performed using clove and cinnamon extract. Two types of tapioca starch based food packaging films (F1 and F2) were produced. In these F2 film had embedded zinc oxide nanoparticles in it whereas, F1 was used as control food packaging film without any nanoparticles. These films were used to wrap sweet lime segments and their advantages were tested via functional properties, characterization and quantitative assessments. The procedure was standardized, filmswere developed and physical properties were tested. Tapioca starch film F2 had the least moisture content (10.21%±0.25), swelling index (28.37%±0.14) & solubility (21.63%±0.42), was smooth, flexible and F1 film had the most transparency. F1 hadthe high values of moisture content (11.03%±0.78), swelling