Phyla Nodiflora Derived Silver Nanoparticles In Hydrogel Formulations: A New Approach To Wound Management
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.3s.19Keywords:
Wound Healing, Wound Healing Silver Nanoparticles, Phyla nodiflora, Green Synthesis, Phytopharmaceutical Hydrogel, MalaysiaAbstract
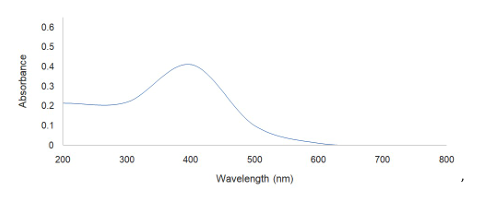
A vital component of healthcare is wound healing, which includes the healing of both acute and chronic wounds. Prolonged inflammation brought on by immunological dysregulation, increased reactive oxygen species, and matrix metalloproteinase activity make chronic wounds difficult to heal. Recent developments release, making it appropriate for the treatment of chronic wounds. The hydrogel's biocompatibility capabilities and wound-healing were shown in In-vitro experiments, suggesting that it may find use in clinical settings for the treatment of chronic wounds in the future. in supplemented with hydrogel dressings antioxidants and immunomodulatory medicines have the potential to improve chronic wound healing. This work investigates the synthesis of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) from the medicinal plant Phyla nodiflora , which has a variety of pharmacological properties, intending to develop a novel phytopharmaceutical hydrogel. Ethanolic extraction was employed to obtain bioactive compounds from Phyla nodiflora , followed by comprehensive phytochemical analysis revealing a notable amount of alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, and phenolic compounds. The green synthesis of AgNPs has been examined by UV spectroscopy, zeta potential measurement, SEM with EDAX, and HRTEM. The hydrogels were evaluated for their pH, viscosity, homogeneity, spreadability, drug content, and release profiles. The optimized formulation demonstrated exceptional spreadability and prolonged medication