Enhancing Breast Cancer Treatment: Investigating the Influence of Polymer Ratios on Luteolin-Loaded TPGS/Poloxamer Micelles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.3s.16Keywords:
Luteolin, TPGS, Poloxamer, Optimization, Micelle, Breast cancerAbstract
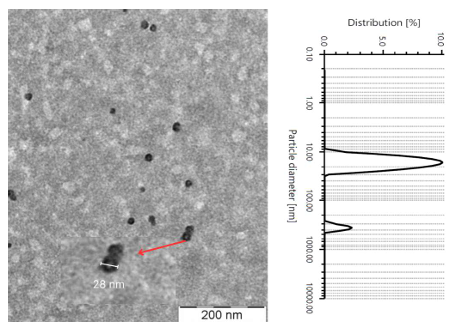
Luteolin is a widely studied flavonoid recognized for its ability to sensitize multidrug-resistant cells and anti-cancer properties. However, its clinical applications is hindered by challenges arising from its limited solubility and bioavailability. To address this issue, a synergistic approach combiningluteolin with vitamin E TPGS (TPGS) and poloxamer (Pol) was explored to boost tumour apoptosis and suppress P-glycoprotein. This study aimed to optimize luteolin-loaded TPGS/Pol micelles developed using the film hydration method, followed by lyophilization. Various key factors including the drug: polymer ratio and the TPGS: Pol ratio were examined, with encapsulation efficiency (EE) assessed using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer and particle size measured via dynamic light scattering (DLS). The results revealed that the optimized micelle composed of 1:5 drug: polymer ratio and a TPGS: Pol ratio of 3:1, exhibited a particle size below 40 nm, along with EE of 90%. Additionally, there was a notable increase of 459-fold in the solubility of luteolin-loaded micelle in a critical micelle concentration (CMC) comparison to pure luteolin in water. The TPGS/Pol micelles demonstrated a critical micelle concentration presented the feasibility of TPGS/Pol micelles in improving the therapeutic potential of luteolin, showcasing improvements in EE, particle size, solubility and sustained release behaviour.