A Development of a Novel Co-processed Excipient Comprising of Microcrystalline Cellulose, Xylitol, Mannitol, and Crospovidone for Orally Disintegrating Tablets
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.3s.6Keywords:
Co-processed excipient, formulation, oral disintegrating tablets, optimizationAbstract
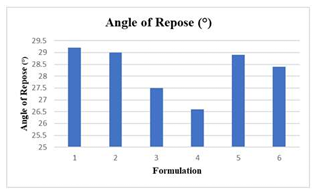
Co-processing an excipient is categorized as a novel methodology applied in the preparation of tablet dosage forms. The main objective of this novel technique is to enhance the flow property of excipients commonly used in the production of tablets which correlates to the direct compression method of tablet production which is highly influenced by the powder characteristics such as dilution potential, compressibility or even flowability. Oral disintegrating tablets (ODT) is becoming a preferred choice in solid dosage form due to its benefits to the patient. It offers a rapid onset of action, improved bioavailability, ease of administration, and improvement in patient compliance to medication, ideal for individuals such as adolescents or elderly that have difficulty in swallowing medications. Although ODTs offers a myriad of merits, there are still some niches where further research may be conducted to improve the formulation, these includes optimizing stability condition, as well as improving mechanical strength of the formulation. The most common method to produce ODTs is through direct compression. Corresponding to the discussion points above, this study was carried out to formulate a novel co-processed excipient that consists of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), xylitol, crospovidone, and mannitol as an orally disintegrating tablet dosage form. The study was conducted in 2 stages. The first stage involves developing 6 different formulations of ODTs that differs in the percentage of co processed excipients such as crospovidone or croscarmellose sodium. Following Stage 1 will be the characterization tests. These includes pre-, and post- compression tests respectively to evaluate the standard of each formulation. Formulation 3 that consist of 72% MCC, 10% xylitol, 10% mannitol, and 8% crospovidone was selected as the optimum co-processed excipient formulation as it achieved fastest disintegration time in comparison to the remaining formulations and was tested with dissolution test to identify the efficiency of drug release. Besides, Formulation 3 also portrayed desired results in other evaluation tests such as friability test weight variation test and hardness test. Co-processed excipient that is characterized by an improve in functionality and disintegration process is beneficial in the application of oral disintegration tablets.