In Silico Identification and Gene Expression Analysis of SNAC Subgroup of NAC Superfamily Members in Zea mays
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2024.1.2Keywords:
NAC genes, SNAC sub-family genes, Abiotic stresses, Zea maysAbstract
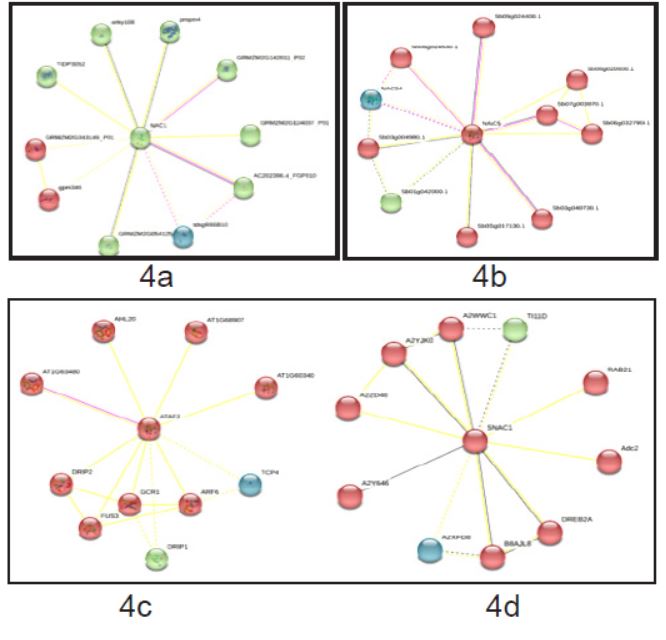
Stress-related NAC (NAM, ATAF1-2 and CUC2) genes, known as SNAC sub-family have been identified in four different species such as Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Sorghum bicolor and Zea mays using the tools of bioinformatics. These genes have been characterized by finding out their introns, exons, cis-regulatory elements, sub-cellular localization, highly conserved motifs, and motif signatures. Phylogenetic tree has been constructed using protein sequences, calculated synonymous to non-synonymous substitution rates (Ka/Ks) of SNAC paralogs and generated 3-dimensional protein models. Predicted SNAC homologs in maize genome have been studied by analysing the synteny of ZmSNAC genes with NAC genes in Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa and Sorghum bicolor. miRNA binding sites have been predicted and analysis of cis-regulatory elements in the promoter regions of SNAC genes in the four plant species has been performed. Identification of SNAC transcription factor homologues in the four plant species and their comparative analysis may provide a basis for further characterization of SNAC transcription factors in various other plant species. Available data have been mined for gene expression analysis under different abiotic stress conditions which displayed up- and down-regulations indicating apparent involvement of SNAC genes during abiotic stress responses.