Effects of Mitragyna Speciosa (Korth.) on macrophage immune responses
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.4s.99Keywords:
Mitragyna speciosa, Macrophages, Anti-inflammatory, Nitric Oxide, CytokineAbstract
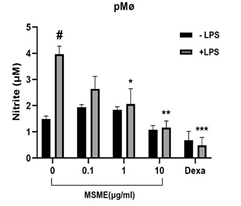
Mitragyna Speciosa (Korth.) or Kratom is an Asian tropical plant that exhibits medicinal benefits, including antioxidants, antibacterial, and antinociceptive effects. This study aimed to explore the immunomodulatory effect of M. speciosa methanolic extract (MSME) on peritoneal isolated primary macrophages (pMø) and murine-derived macrophages, RAW264.7 cell line. The cytotoxicity effect of MSME on both RAW264.7 cells and pMø was determined by a cell viability test using a Cell-Titer Blue assay. Furthermore, the effects of MSME on the secretion and expression of mediators of the immune system, including nitric oxide (NO), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and cytokines in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- stimulated macrophages were evaluated by Griess assay and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRTPCR). In addition, the effect of MSME on the phagocytic activity of LPS-stimulated macrophages was determined by a neutral red uptake assay. The cytotoxicity analysis shows stable cell viability above 80% except when treated at a high MSME concentration (>100 µg/ml). MSME exhibited antiinflammatory effects in LPS-stimulated macrophages, as shown by a significant inhibition of NO secretion and the expression of iNOS, Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), and Interleukin-6 (IL-6). Furthermore, the extract also significantly reduced the phagocytic capacity of both LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells (36.71±6.46; MSME 100 ug/mL; p=0.0266) and pMø (42.76±10.18%; MSME 10µg/mL; p=0.0142). In conclusion, our findings suggest that treatment of MSME in LPS-activated macrophage attenuated immune responses through inhibition of phagocytic ability, reduction of NO and iNOS levels, and downregulation of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 gene expression.